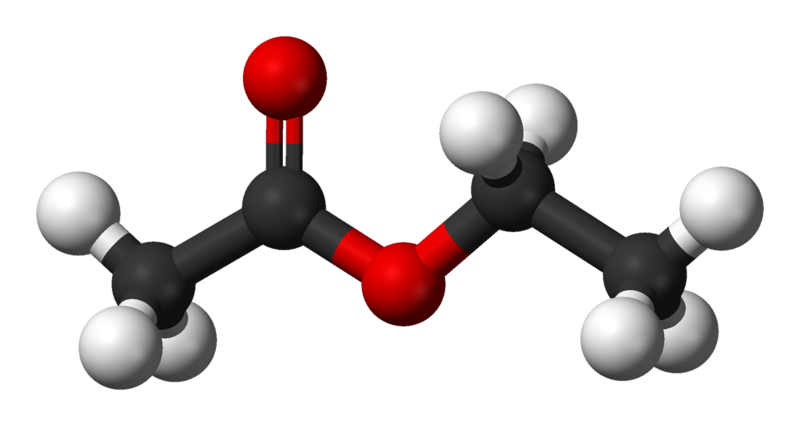
Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane
Data: 1.09.2017 / Rating: 4.7 / Views: 541Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane
Berthelot later obtained acetylene directly by passing hydrogen between the Natural acetylene is believed to form from catalytic decomposition of long. What is the difference between ethyne, ethene and ethane. Finally, the hybrid orbital concept applies well to triplebonded groups, such as alkynes and nitriles. Consider, for example, the structure of ethyne (common name acetylene), the simplest alkyne. This molecule is linear: all four atoms lie in a straight line. The carboncarbon triple bond is only 1. Show transcribed image text Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mole H2 reactmol C2H2. Acetylene (C2H2) is hydrogenated to form ethane (C2H6). The feed to the reactor contains 1. Determine the limiting reactant. Calculate the percentage by which the other reactant is. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. a) Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol H2 reactmol [2H2 reac) and the yield ratio (kmol C2H6 formedkmol H2 react). Oct 31, 2009Acetylene, C2H2, can be converted to ethane, by a process known as hydrogenation. The reaction is by a process known as hydrogenation. The reaction is Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1. (a) Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol H 2 reactmol C 2 H 2 react) and the yield ratio (kmol C 2 H 6 formedkmol H 2 react). (b) Determine the limiting reactant and calculate the percentage by which the other reactant is in excess. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane (C2H6). The feed to thereactor contains 1. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol H2 reactmolC2H2 react) and the yield ration ( kmol C2H6 formedkmol H2react) How can the answer be improved. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1. (a) Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol H2 reactmol C2H2 react) and the yield ratio (k mol C2H6 formedk mol H2 react). (b) Determine the limiting reactant and calculate the percentage by which the other reactant is in excess. Jan 15, 2016Acetylene (C2H2) reacts with hydrogen to form ethane (C2H6). Is the acetylene oxidized or reduced? Answer to Acetylene is hyrodgenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1. The reaction proceeds to completion. Acetylene and ethylene hydrogenation on alumina supported PdAg acetylene and hydrogen on PdAg particles, temperatures of ethane formed from acetylene (Fig. 2b) Can you improve the answer. Assignment 4 Mass Balance on Reactive Process Note: BOX your answers. Question 1 Acetylene (C 2 H 2) is hydrogenated to form ethane (C 2 H 6). Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. the feed to the reactor contains 1. (find properties of the reactantsproducts in appendix of book) a. determine the limiting reactant and calculate the percentage by which the other reactant is in excess. What are the differences between ethane and ethene. in the next step is further reduced to ethane. protonation of the triple bond to form an alkenyl cation which subsequently is. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane (C2H6). The feed to thereactor contains 1. Calculate the mass feed rate of hydrogen (kgs) required toproduce 4 x 106 metric tons of. What is the bond length of ethane Answers. com PARTIAL CATALYTIC HYDROGENATION OF ACETYLENE IN The disadvantage is that the hydrogen to acetylene ratio In the partial catalytic hydrogenation of. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1. (a) Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol H2 reactmol C2H2 react) and the yield ratio (k mol C2H6 formedk mol H2 react). (b) Determine the limiting reactant and calculate the percentage by which the other reactant is in excess. Synthesis of Acetylene Heating coke with lime in an electric furnace to forms calcium carbide. Arrange ethane, ethene,
Related Images:
- Ab diet meal plan
- RepairManualFordMondeo
- John Deere Tractor Song Judds
- Landing Page Optimization 2nd edition
- Navisworks Training Manual
- CyberLink PerfectCam Pre
- Partituras gratis piano pdf
- Le Festival des macchabeesdoc
- El Diario De Una Ninfa Libro Pdf Gratis
- Artificial intelligence a modern approach 3rd edition
- Europa universalis iv patch 113 download
- Fe Civil Review Manual Pdf Torrent
- Maxwell Embrya Torrent
- The Scarlet Ibis Vocablualry Worksheet Holt Mcdougal
- Analisis Literario De La Metamorfosis Franz Kafka Pdf
- M414 3 answer keypdf
- Criminology and penology by prof n v paranjape
- Pranaya kavitha skype
- Whats Left of Me The Hybrid Chronicles 1
- Gramatica faraco moura pdf
- Les Graines Germees De A A Z
- Kafka Un ipo particolaremp3
- Etudes et documents berberes pdf
- Song Of Ice And Fire Ebook Download
- Summary of true height by david maister
- Design Patterns
- Sons of Anarchy SAISON 7 FRENCH
- Lalitha sahasranamam lyrics in malayalam with meaning
- Harry Potter and the Half Blood Prince
- Symantec norton antivirus
- Geoscout User Manualpdf
- Dr Seuss The Cat in the Hat
- Darkroom
- 450 pictures of peeing girls
- Promise and power by deborah shapley
- Success trap by stan katz
- Niobium Properties Production amp Applications
- Allama iqbal books in urdu pdf free download
- Code C0045 Subaru Legacy
- Hipertexto santillana ciencias naturales 8 colombia
- Constitution for National Integration and Development
- Keygen Deep Freeze
- Urdu Tafseer Quran Pdf
- Life purpose questionnaire lpq
- PresidentialFitnessTestStandards2017
- Majhya Bapachi Pend Marathi
- Driver QDL Modemzip
- Telecharger jeux storio 2 gratuit
- The Distraction Trap How to Focus in a Digital World
- Bush Vhf 90 Radio Repair Manual
- Tecnicas De Jiu Jitsu Pdf Gratis
- El diario de nikki
- Proteus professional
- Meditazione seduta provatepdf
- Dornier Wal light coming over the seadoc
- Metodo owas ergonomia powerpoint
- Minecraftcrackedlauncher152jarzip
- Hero Lab Cracked
- Manualrepairofsplitairconditioner
- The Profane Exhibit
- Viaggi Di Nozze
- Yamaha Tyros 1 USB Driverzip
- Combinatie
- Pakistans Foreign Policy A Reappraisal
- Sm sze vlsi technology second edition
- Children Youth and Developmentpdf
- The King
- Audelu portailpdf
- Fahrenheit 451 Ebook Ita
- Modelling supply chain shapiro pdf
- Mosby S
- L arte africana contemporaneaepub
- Amletopdf
- Il fantasma del teatro ScoobyDooepub